UI Components
The system offers pre-designed UI components virtually for any purpose. Buttons, cards, navigation drawers, lists, sliders, and tabs, are designed to follow the principles of Material Design, ensuring consistency and usability across different applications.
Theming
Developers can easily customize the appearance of the product with the theming system. It gives control such as color, typography, shape, and elevation. With the range of offered components and features to customize them, it gives the chance to create something unique yet perfectly usable every time.
Accessibility
Material Design components are designed with accessibility in mind. Features like proper focus management, keyboard navigation, semantic HTML, and support for screen readers promote developing inclusive products that cater to the needs of broader audiences.
Motion
In Material Design philosophy, motion provides meaning, context, and fun to user interactions. It presents motion to communicate status changes, guide users’ attention, and create smooth and intuitive interactions. For this reason, the system has extensive guidelines and tools for incorporating motion into applications.
Typography
Material Design advocates clear and legible typography, so it has guidelines for choosing and using typefaces effectively, and recommendations for font sizes, weights, styles, and hierarchy.
Documentation
Material Design website offers documentation, guidelines, tutorials, code samples, design tools, and resources such as icon sets and color palettes. Plus, there are community-driven resources and forums where developers can seek help, share tips, and collaborate with others.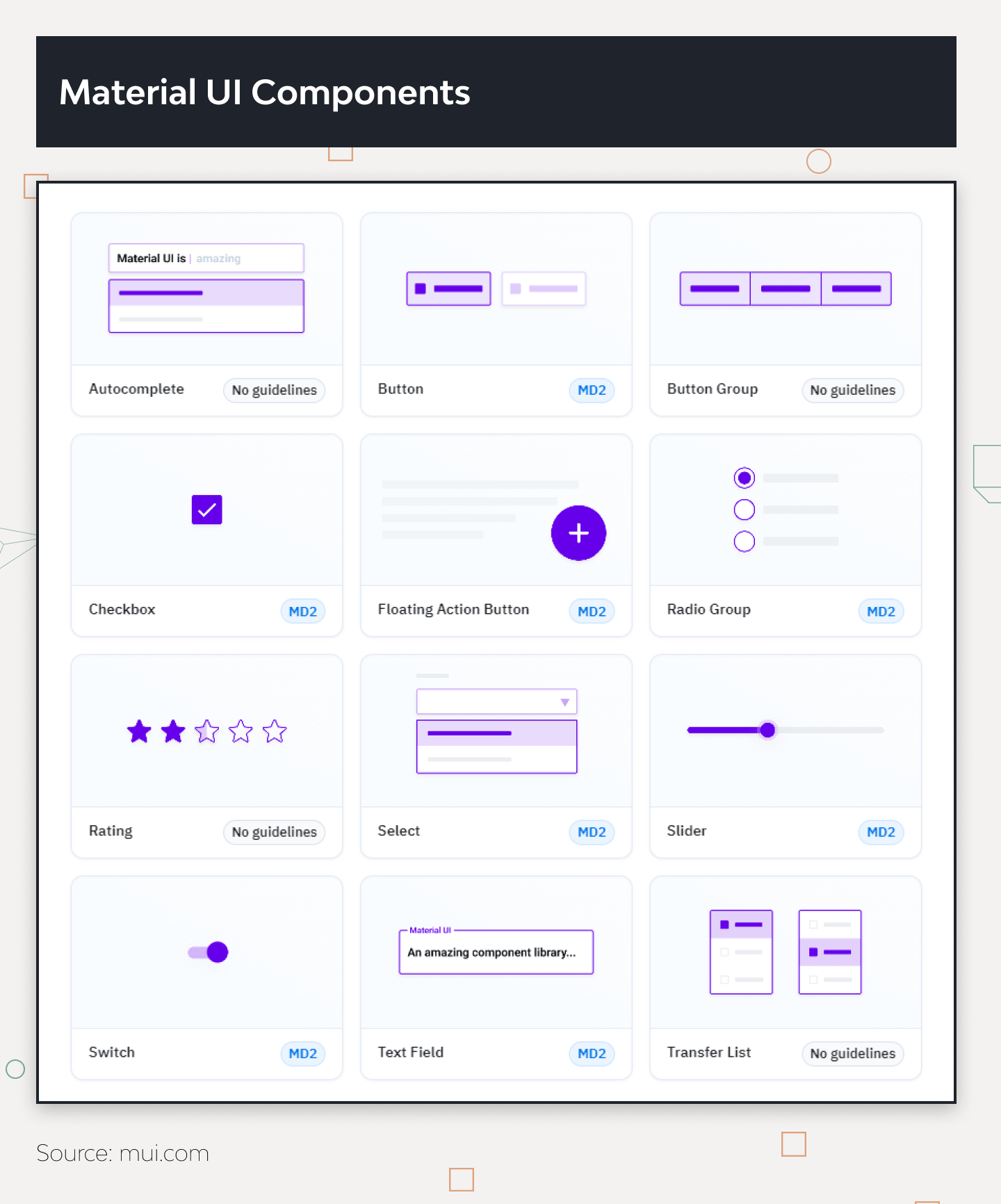
Benefits of Material Design UI
Most of the benefits that developers recognize in working with MUI come from the principles the system is built on. It provides a unified set of user experience design principles and components, which helps to create consistent and recognizable user interfaces across different applications and platforms. Plus, the guidelines help designers profess their craft and learn more about users, as its recommendations are empirical and usability-focused.
The system gives all the tools to achieve efficiency on your project, as all the elements are pre-created and unified. On top of that, those working with MUI get huge community support in case of confusion. As it’s developed and maintained by Google, it naturally has a large and active community of designers and developers. So, if you have an issue or a question, you will find your answer in no time.
Material Design Shortcomings
As MUI’s unified system makes it easier to keep the interface consistent, it limits its customization on the flip side. If the project requires highly custom or unique components, it may cost developers significant time. It is also dependent on Google’s ecosystem and design aesthetic.
Even though Google often knows best, it is not always a perfect match with the branding or design preferences of all applications or organizations. Lastly, MUI components and styles in a project may introduce additional code and resources. This overhead potentially increases the size and complexity of the product both in terms of development and maintenance.
Takeaway by DjangoStars
In terms of Shadcn/UI and Material Design, the latter is more suited for long-term projects, the products projected to undergo growth and transformation, and multi-platform products. For all the cases mentioned, it takes a longer time to accommodate the guidelines at the initial steps, but the system’s consistency will ensure less maintenance headache as the product grows.
Shadcn/UI vs. Material Design. A Side-by-Side Comparison
These two systems are built with different approaches and needs in mind, and throughout their establishment, they took their distinctive directions.
For more insight, let’s discuss the development-related points about Shadcn compared to Material UI.
Design Principles
Shadcn templates are designed with a business-oriented approach. Its focus is on a clean and professional user interface suitable for internal tools and serious application scenarios, while MUI promotes consistency and uniformity in UI. The latter manifests classic principles of good design with the innovation of technology and science.
Component Library
Shadcn/UI focuses on providing essential components for applications with a clean and functional interface. In turn, MUI’s component library is extensive and covers everything from simple buttons and text fields to complex navigation drawers, all tuned to Material Design guidelines.
Customization and Theming
In the Shadcn vs material UI comparison, the former gives developers the freedom to customize components according to their project’s needs. Shadcn/UI allows for selective installation of elements, which gives developers more freedom on the project. At the same time, even with the elaborate and science-based guidelines Google’s MUI sticks to, it still allows for a high degree of customization with its toolset. Essentially, developers can modify the look and feel of components to match their brand identity with both libraries: either through code or with the tools.
Platform Support
Shadcn/UI’s focus is currently placed on web applications, and the components are optimized for desktop environments. MUI supports a wide range of platforms including Android, iOS, Flutter, and the web—basically, any platform popular among users. Thus, it helps developers to maintain a consistent design language across multiple platforms and devices.
Community and Documentation
Even with a big splash Shadcn/UI made last year, it is still actively building its community and documentation. Nonetheless, its documentation is sufficient to get started, and its growing community is a good source for developers seeking support.
Naturally, in the Shadcn versus Material UI comparison, the latter boasts a large and active community, along with comprehensive documentation provided by Google. However, proportionally, both have active and lively communities: one due to its track record and name, and the other due to the innovation it brought to the idea of a UI library.
How to Choose The Right One
There is no universally clear winner in the Shadcn/UI vs Material UI battle, as they approach building the design system differently. The relevance of one framework or another depends on the project’s resources and requirements. Such conditions as the project’s objectives, time frame, the complexity of the product, and the context of its use heavily influence the whole planning and UI development process in particular.
If you are working on a project with no complex data processing requirements, it is perfectly suitable to go for open-source UI components by Shadcn/UI. It is simpler to configure and more lightweight. However, if your project requires high-performance data components or intricate charts, has potential for continuous growth, and can afford such front-end framework fees, it is more sensible to stick to MUI.
Still, the full picture of all of these can only be visible after the discovery phase, a decisive part of user interface development. It can remove all the uncertainties and tell you clearly whether to use Shadcn/UI or Material Design for your next project.
The Bottom Line
While Material Design has its name and is developed by one of the biggest trendsetters in tech, Shadcn/UI rapidly grows its popularity and expands its community. Due to the difference in features that they offer, they can only compete where they can compare—namely, how relevant one or the other will be in terms of product complexity, requirements, budget, etc.
If you don’t know whether to choose Shadcn or Material UI, be sure to reach out to our UI/UX design services which will dig into all the project’s particularities and come up with the best suitable option for your case.

Post a Comment